Rhizophora mucronata
Rhizophora mucronata, also known as the Red Mangrove, is a crucial tree in mangrove forests. This tree is distinctive and highly adaptive, playing a crucial role in protecting coastal areas.


The Red Mangrove is a small to medium-sized evergreen tree that grows along the banks of rivers, reaching a height of about 20 to 25 meters. Along the seashore, a more typical height is 10 or 15 meters. The tallest trees are closest to the water, and the shorter ones are further inland.
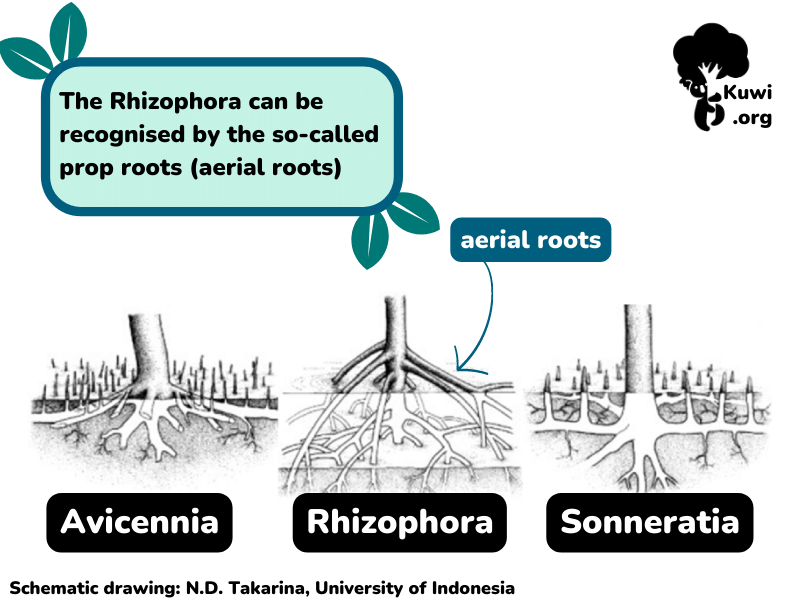
The species has very distinctive prop roots (aerial roots) that firmly anchor the tree in the muddy substrate, providing protection against the relentless forces of tides and waves along the coast.
The leaves of Rhizophora mucronata are equally remarkable. They display an elliptical shape, with a glossy green hue and a pointed tip that inspired the species name ‘mucronata.’ These leaves master the art of survival, excreting excess salt through specialized glands and enduring both dehydration and flooding.
Habitat and Distribution
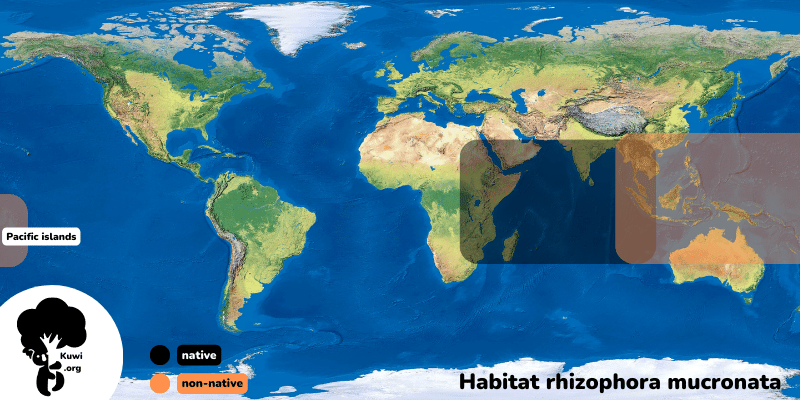
The Red Mangrove prevails dominantly along tidal areas, where the restless dance of the tides exposes it to the harsh reality of the coastal world. Its distribution encompasses a wide range of tropical and subtropical regions, from the coral-rich shores of the Indian Ocean to the tranquil lagoons of the Pacific Ocean. This geographical ubiquity demonstrates the unparalleled ability of the species to adapt and thrive in diverse environments.
The tree originates from an extensive area of tropical and subtropical coastal regions. It proudly calls regions of the Indian Ocean, including the coasts of East Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, the Indian subcontinent, and Southeast Asia, its original home. These coastal landscapes, characterized by warm waters and brackish intertidal areas, have created the ideal conditions for the survival and evolution of the Red Mangrove.
Uses of Red Mangrove
Rhizophora mucronata serves a multitude of purposes. It aids in preventing coastal erosion and contributes to the restoration of mangrove habitats. The wood is used for firewood, construction, as posts, poles, and in the making of fish traps. The fruits are edible, either cooked or their juice converted into wine, while young shoots are consumed as vegetables. The bark is used in tanning, and both the bark and leaves yield dye. Various parts of the plant are employed for applications in traditional medicine.
Ecological Engineer
In addition to its own survival, Rhizophora mucronata plays a crucial role as a Biobuilder. The intricate root system acts as a natural buffer, protecting coastal communities from erosion and storms. Moreover, these roots provide a refuge for a variety of aquatic organisms, creating a complex web of life that ripples throughout the entire mangrove ecosystem.
Conservation and Future Perspectives
Despite the resilience of Rhizophora mucronata, it is not immune to threats from human activities such as habitat loss, deforestation, and pollution. Conservation efforts are in place to preserve and restore the habitat of this valuable tree, as people recognize its significance.
The Red Mangrove stands as an example of adaptability and natural coherence in the environment. With its robust roots anchoring the soil, it resembles a protective guardian of the coastline, embodying the resilience of mangrove forests. It is our collective responsibility to ensure that this remarkable tree continues to adorn our shores and inspires future generations.
IUCN Red List

Plant this tree


